本系列为 Three.js journey 教程学习笔记。
Scroll based animation 基于页面滚动的动画
本节我们将学习基于页面滚动的动画。很好的将之前所学的内容做一个复习和运用。
我们会把 WebGL 部分固定到页面中,随着页面的滚动 WebGL 中也随之相应的产生动画效果。这种联动的效果会带来非常好的体验,并且也会让你的页面看起来很高级很有未来感。联动的效果主要是使用 camera 的角度变化来实现。并且最后会加入一些滚动到某个区域后的动画效果。
准备
因为我们使用固定视角的相机,所以 OrbitControls 就不再需要了。我们需要设置一些 HTML 内容,并且撑满屏幕高度
HTML 结构如下
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>scroll based animation</title>
</head>
<body>
<canvas id="mainCanvas" class="webgl"></canvas>
<section class="section">
<h1>Hello</h1>
</section>
<section class="section">
<h2>My projects</h2>
</section>
<section class="section">
<h2>Contact me</h2>
</section>
<script src="<%= path %>" charset="utf-8"></script>
</body>
</html>
CSS 代码如下,我们设置了页面背景色,设置 section 高度为 100vh,设置好布局
body {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
background-color: #263238;
}
.webgl {
position: fixed;
top: 0;
left: 0;
outline: none;
}
.section {
padding-left: 10%;
padding-right: 10%;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
height: 100vh;
font-size: 7vmin;
position: relative;
color: #fff;
}
section:nth-child(odd) {
justify-content: flex-end;
}
一个可以滚动的页面就完成了
我们在 ts 文件中再绘制一个基础的小立方体和灯光
import * as THREE from 'three'
import './style.css'
import * as dat from 'lil-gui'
import stats from '../common/stats'
import { listenResize, dbClkfullScreen } from '../common/utils'
// Canvas
const canvas = document.querySelector('#mainCanvas') as HTMLCanvasElement
// Scene
const scene = new THREE.Scene()
// Size
const sizes = {
width: window.innerWidth,
height: window.innerHeight,
}
// Camera
const camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(75, sizes.width / sizes.height, 0.1, 100)
camera.position.set(0, 0, 6)
/**
* Objects
*/
const cube = new THREE.Mesh(new THREE.BoxGeometry(1, 1, 1), new THREE.MeshStandardMaterial())
scene.add(cube)
const directionLight = new THREE.DirectionalLight()
directionLight.position.set(1.5, 1, 1)
const ambientLight = new THREE.AmbientLight(new THREE.Color('#ffffff'), 0.2)
scene.add(ambientLight, directionLight)
const directionLightHelper = new THREE.DirectionalLightHelper(directionLight, 2)
scene.add(directionLightHelper)
// Renderer
const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({
canvas,
antialias: true,
alpha: true,
})
renderer.setSize(sizes.width, sizes.height)
renderer.setPixelRatio(Math.min(window.devicePixelRatio, 2))
listenResize(sizes, camera, renderer)
dbClkfullScreen(document.documentElement)
// Animations
const tick = () => {
stats.begin()
// Render
renderer.render(scene, camera)
stats.end()
requestAnimationFrame(tick)
}
tick()
/**
* Debug
*/
const gui = new dat.GUI()
gui.add(directionLightHelper, 'visible').name('directionLightHelper visible')
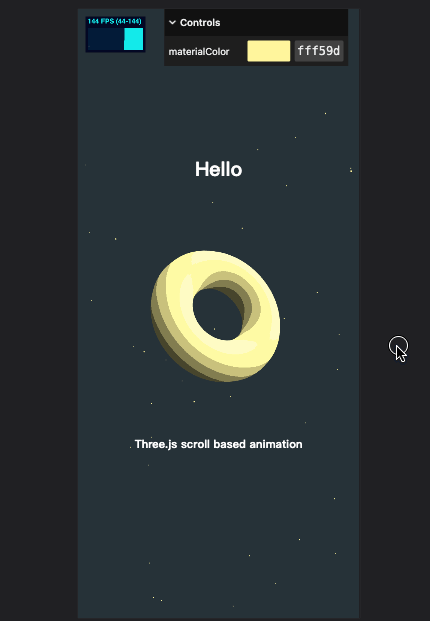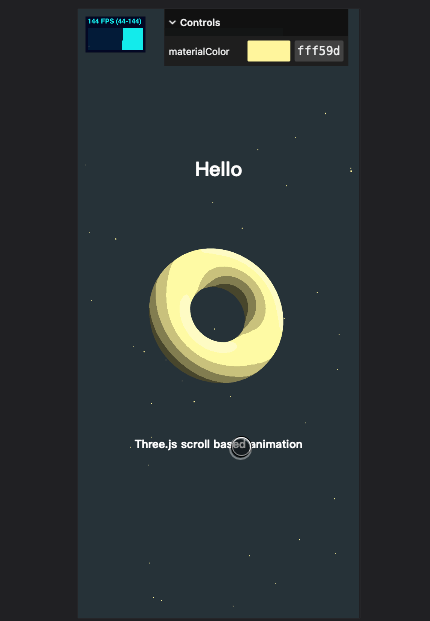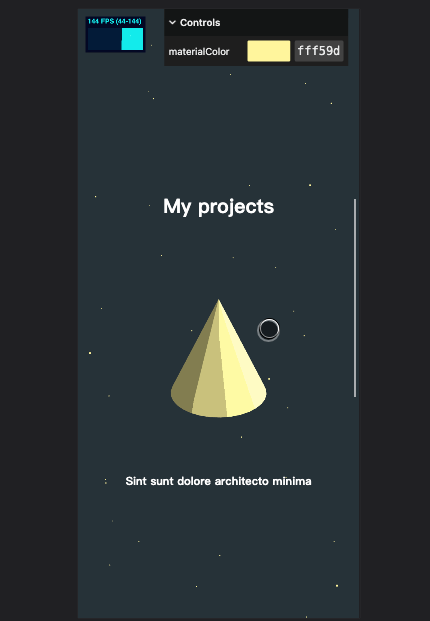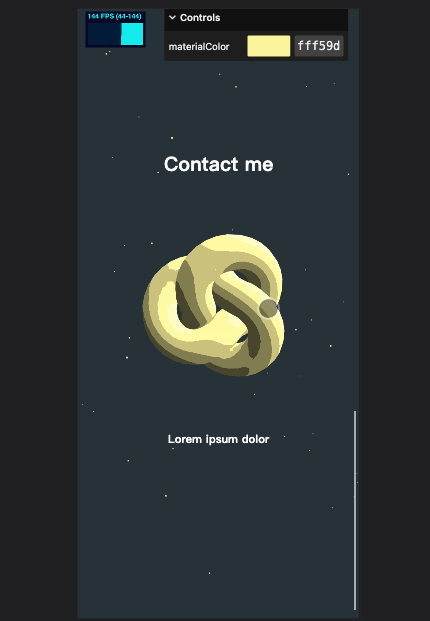
效果如下
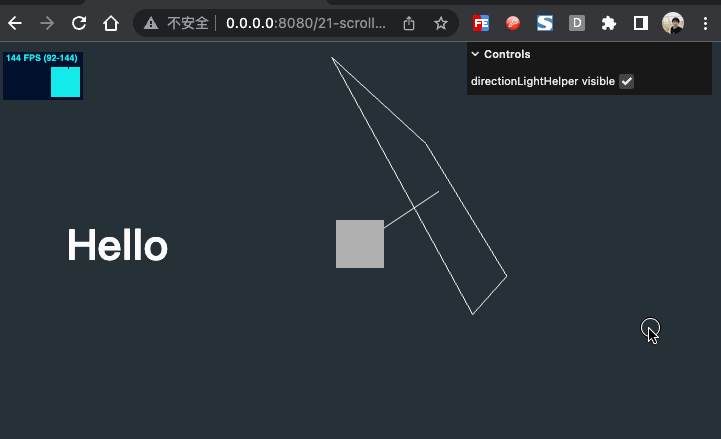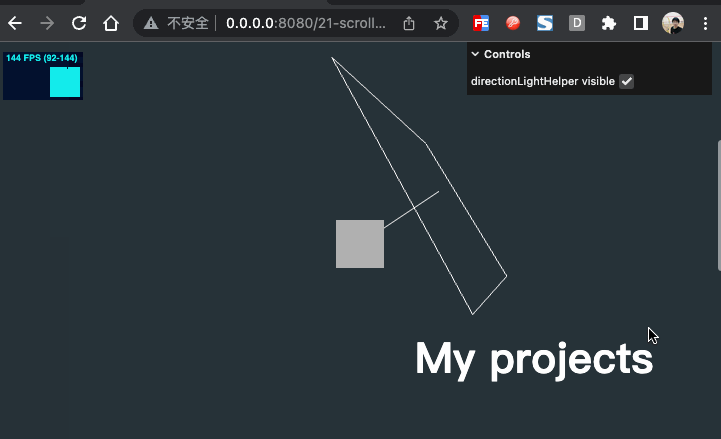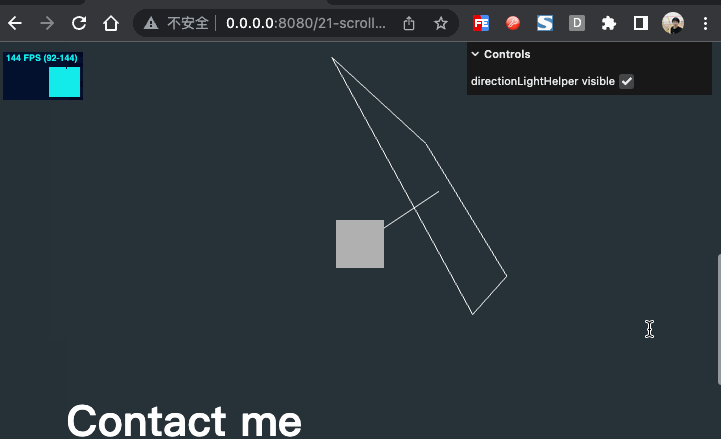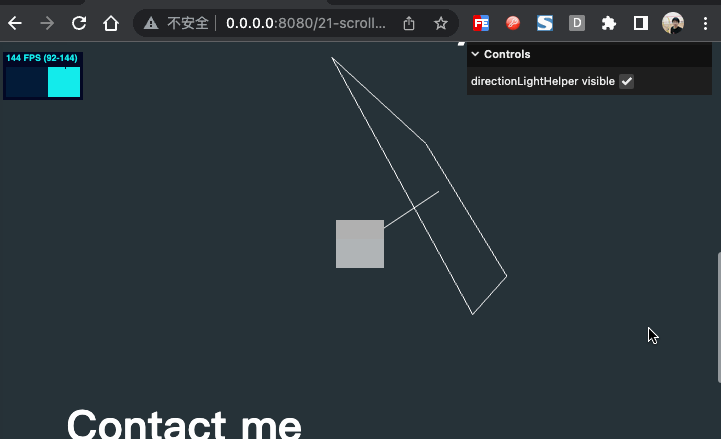
物体
几何体
我们将原有的立方体移除,使用 Three.js 内置的 圆环 TorusGeometry、圆锥 ConeGeometry 和圆环扭结 TorusKnotGeometry
// Meshes
const mesh1 = new THREE.Mesh(
new THREE.TorusGeometry(1, 0.4, 16, 60),
new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: '#ff0000' }),
)
const mesh2 = new THREE.Mesh(
new THREE.ConeGeometry(1, 2, 32),
new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: '#ff0000' }),
)
const mesh3 = new THREE.Mesh(
new THREE.TorusKnotGeometry(0.8, 0.35, 100, 16),
new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: '#ff0000' }),
)
scene.add(mesh1, mesh2, mesh3)
效果如下
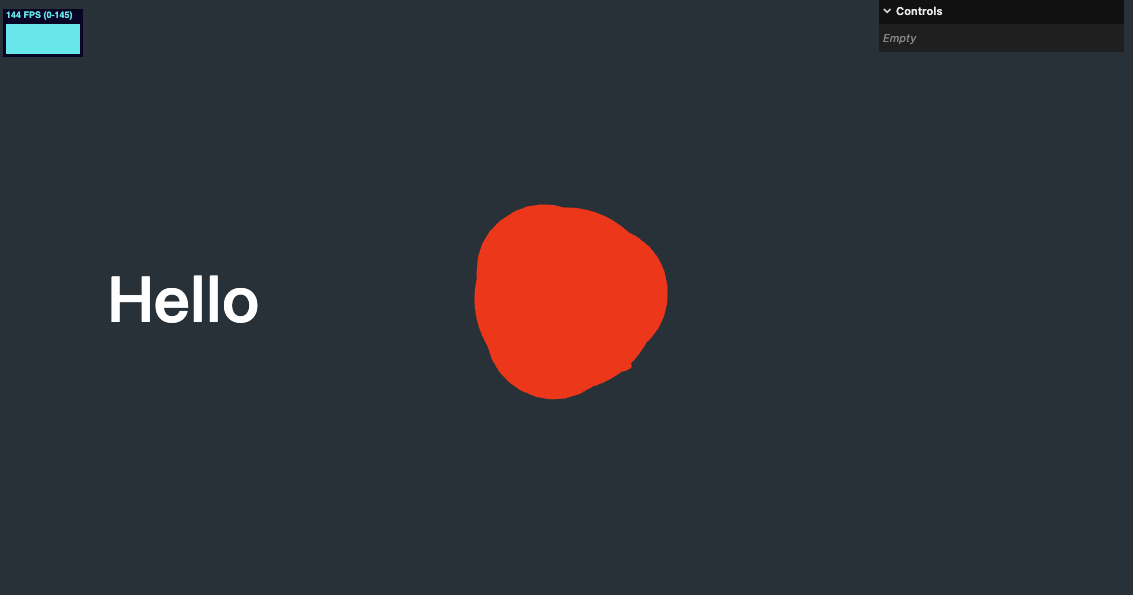

别着急,随后我们修改几何体的为位置和相机视角
接下来我们设置材质
材质
我们使用卡通材质
// Material
const material = new THREE.MeshToonMaterial({ color: parameters.materialColor })
// Meshes
const mesh1 = new THREE.Mesh(new THREE.TorusGeometry(1, 0.4, 16, 60), material)
const mesh2 = new THREE.Mesh(new THREE.ConeGeometry(1, 2, 32), material)
const mesh3 = new THREE.Mesh(new THREE.TorusKnotGeometry(0.8, 0.35, 100, 16), material)
scene.add(mesh1, mesh2, mesh3)

灯光
我们把刚刚移除的灯光重新加回来
/**
* Lights
*/
const directionalLight = new THREE.DirectionalLight('#ffffff', 1)
directionalLight.position.set(1, 1, 0)
scene.add(directionalLight)
const ambientLight = new THREE.AmbientLight('#ffffff', 0.28)
scene.add(ambientLight)
现在效果好多了

const gui = new dat.GUI()
gui.addColor(parameters, 'materialColor').onChange(() => {
material.color.set(parameters.materialColor)
})
增加 gui 就可以在右上角调节颜色了
Gradient texture 渐变纹理
// Texture
const textureLoader = new THREE.TextureLoader()
const gradientTexture = textureLoader.load('https://gw.alicdn.com/imgextra/i1/O1CN01Kv3xWT1kImpSDZI8n_!!6000000004661-0-tps-5-1.jpg')
gradientTexture.magFilter = THREE.NearestFilter
// Material
const material = new THREE.MeshToonMaterial({
color: parameters.materialColor,
gradientMap: gradientTexture,
})
这个 gradientMap 图片为5个像素点灰阶图片。如下图

这里注意 magFilter 的使用,如果遗忘了复习 Three.js 之 6 Texture 纹理。

位置
Three.js 默认是根据竖直方向的高度定相机视野适配的,高度等比适配
例如我设置如下代码
mesh1.position.y = 4
mesh1.scale.set(0.5, 0.5, 0.5)
mesh2.visible = false
mesh3.position.y = -4
mesh3.scale.set(0.5, 0.5, 0.5)
不管怎么移动窗口,可以看到2个物体距顶部和底部的距离比例不变。如下图
我们移除刚才的测试代码
声明一个物体距离
const objectsDistance = 4
并设置在每个物体上
mesh1.position.y = -objectsDistance * 0
mesh2.position.y = -objectsDistance * 1
mesh3.position.y = -objectsDistance * 2

现在我们只能看到第一个物体
增加一些物体的自转
将几何体放入数组
const sectionMeshes: THREE.Mesh<THREE.BufferGeometry, THREE.MeshToonMaterial>[] = [
mesh1,
mesh2,
mesh3,
]
再一起加入动画
// Animations
const clock = new THREE.Clock()
const tick = () => {
stats.begin()
const elapsedTime = clock.getElapsedTime()
// Animate meshes
sectionMeshes.forEach((mesh) => {
mesh.rotation.set(elapsedTime * 0.1, elapsedTime * 0.12, 0)
})
// Render
renderer.render(scene, camera)
stats.end()
requestAnimationFrame(tick)
}
效果如下

相机与滚动
接下来我们要添加随着页面滚动相机也进行位置变化的效果
首先我们要监听页面的滚动
/**
* Scroll
*/
let { scrollY } = window
window.addEventListener('scroll', () => {
scrollY = window.scrollY
console.log(scrollY)
})
可以看到 log 里已经有了滚动距离
接下来在 requestAnimationFrame 中控制对相机的移动,这里需要注意的是相机的位置移动比例
// Animations
const tick = () => {
// ...
// animate camera
camera.position.setY((-scrollY / sizes.height) * objectsDistance)
// ...
}
HTML 页面滚动距离与相机需要位移的距离相反,因此要添加负号。-scrollY / sizes.height 表示设置相机移动的每个区域为了 1 个单位。但几何体实际位置是 objectsDistance 单位距离,所以最终为 -scrollY / sizes.height) * objectsDistance。
效果如下

几何体水平位置修改
我们将几何体水平位置稍做移动,以适配文字,并将之前对 y 值设置的代码也可以放在这个 for 循环里
sectionMeshes.forEach((item, index) => {
item.position.setY(-objectsDistance * index)
item.position.setX(index % 2 === 0 ? 2 : -2)
})
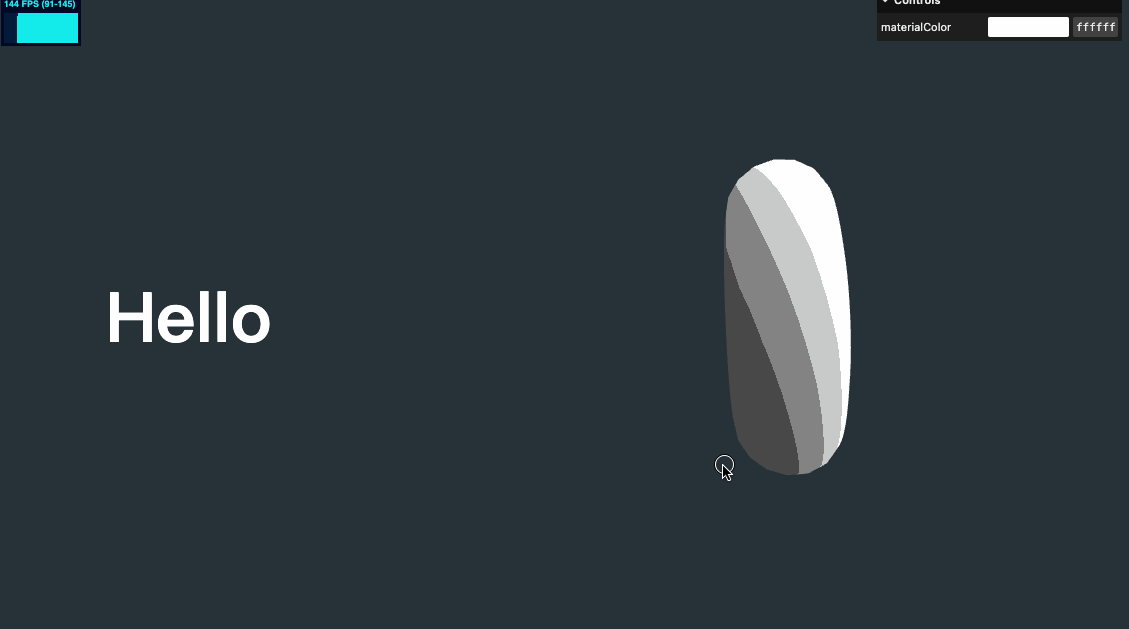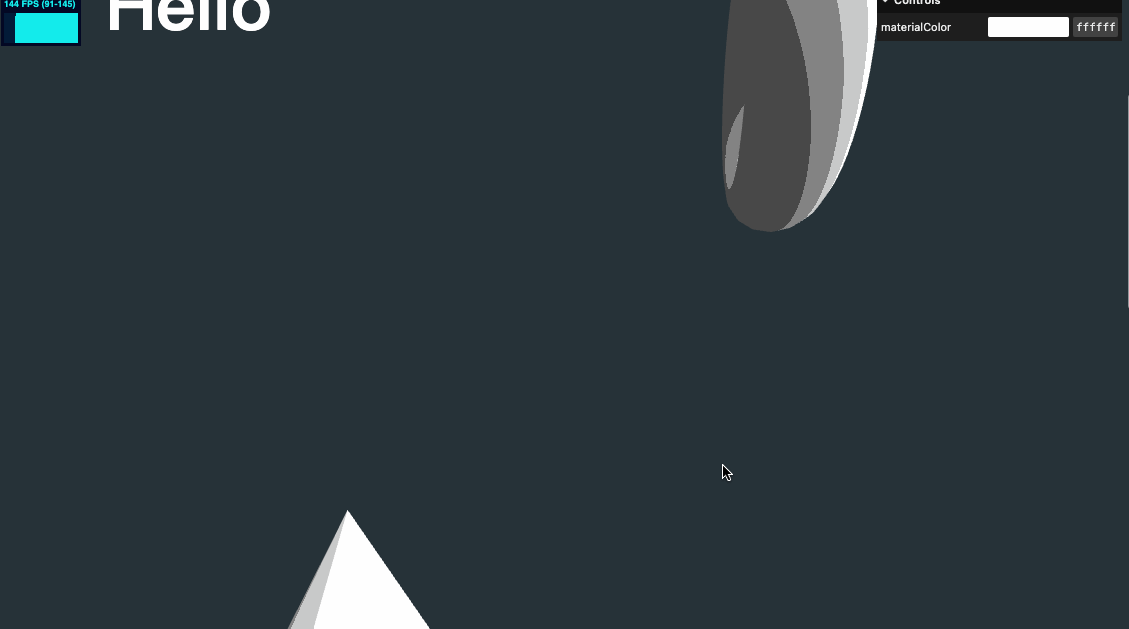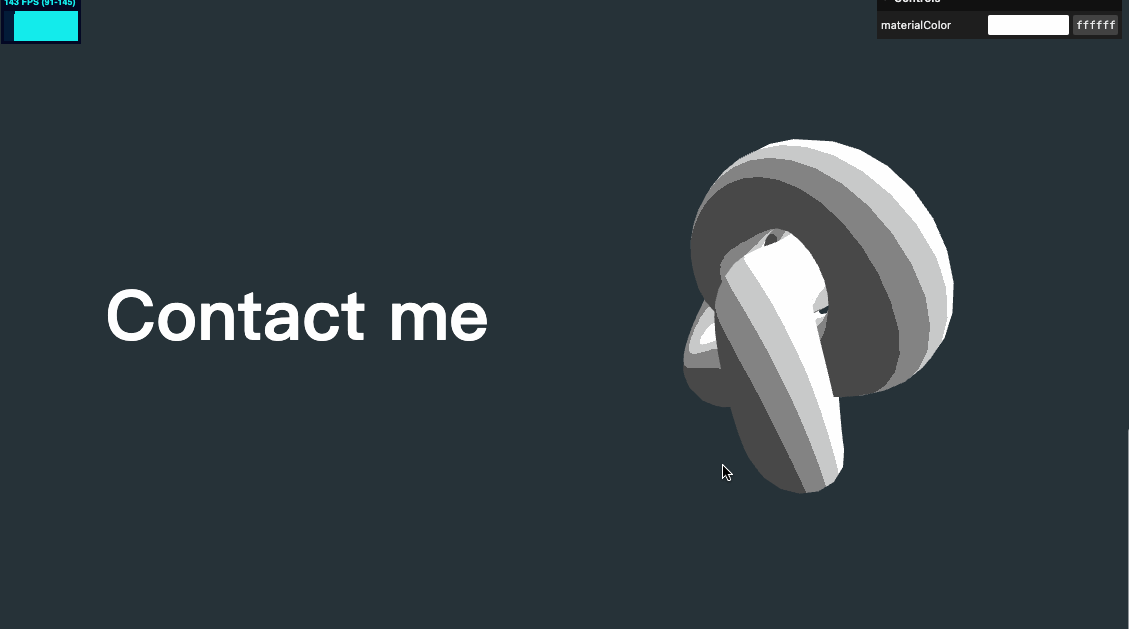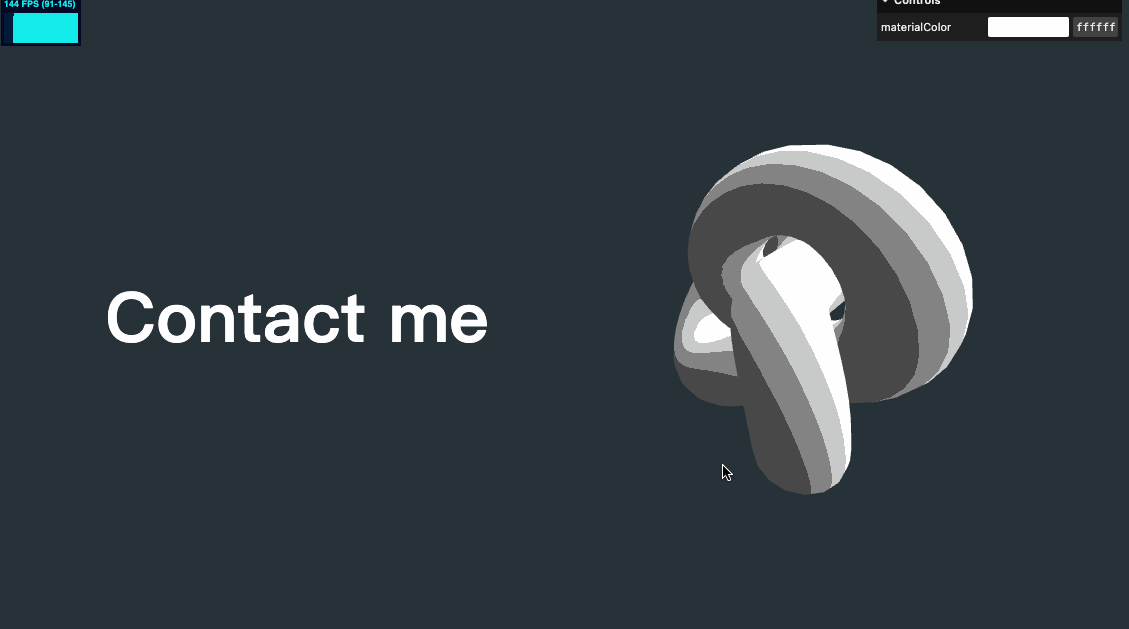
视差效果
我们再增加一点视差效果,当鼠标移动时,几何体的位置稍微进行一点点偏移,更有沉浸感。
我们沿用上一节学到的监听鼠标移动
/**
* Mouse
*/
const mouse: {
x: number | null
y: number | null
} = { x: null, y: null }
window.addEventListener('mousemove', (event) => {
mouse.x = (event.clientX / sizes.width) * 2 - 1
mouse.y = -(event.clientY / sizes.height) * 2 + 1
})
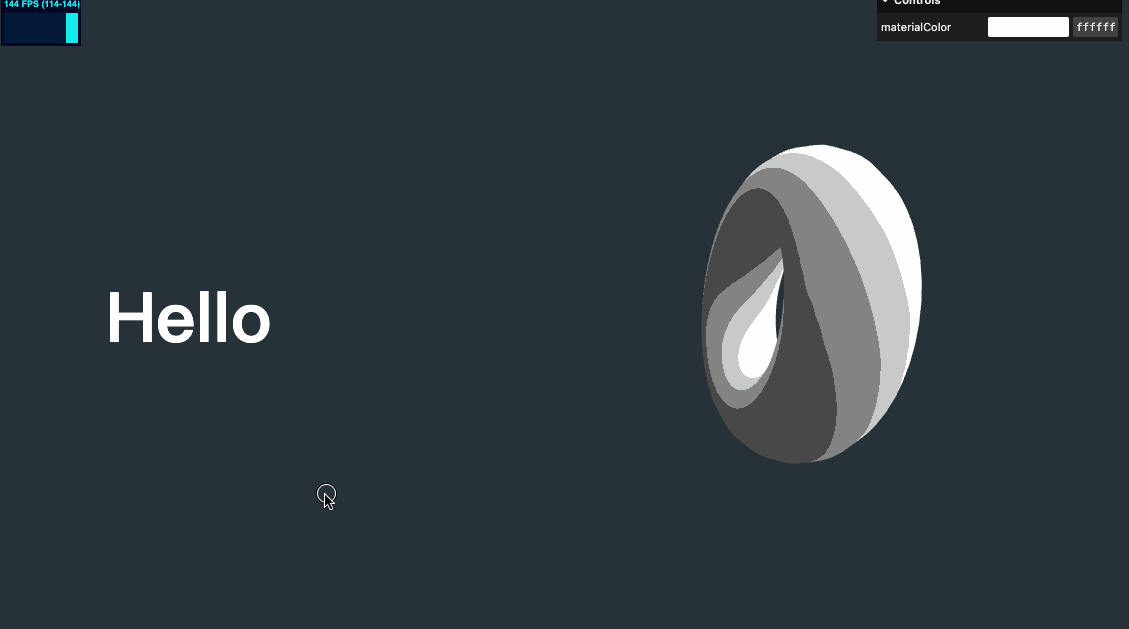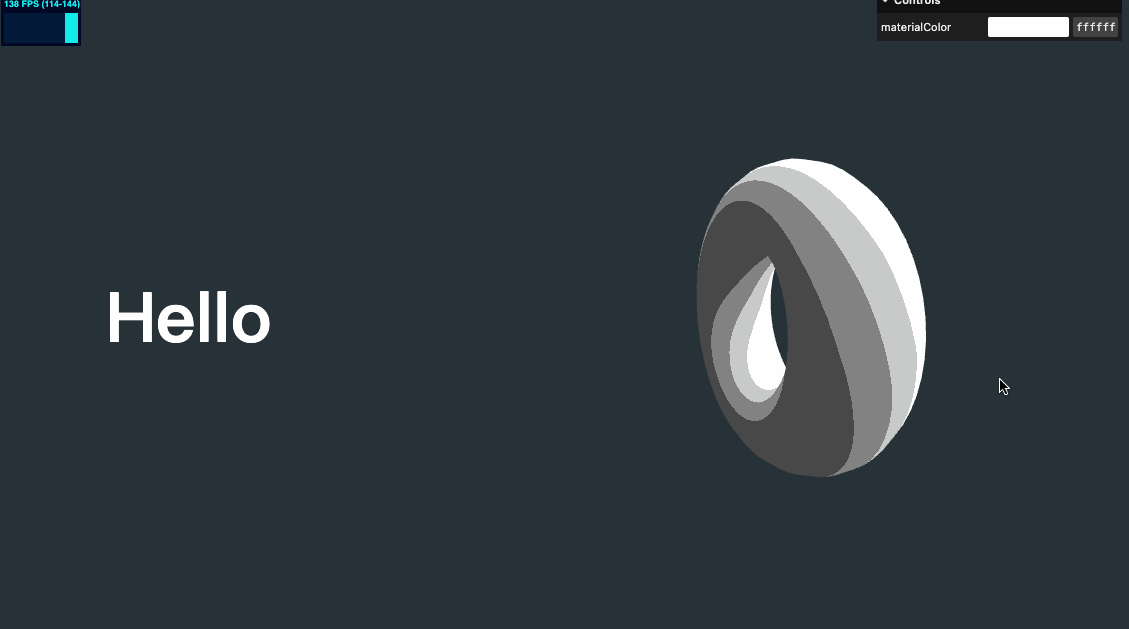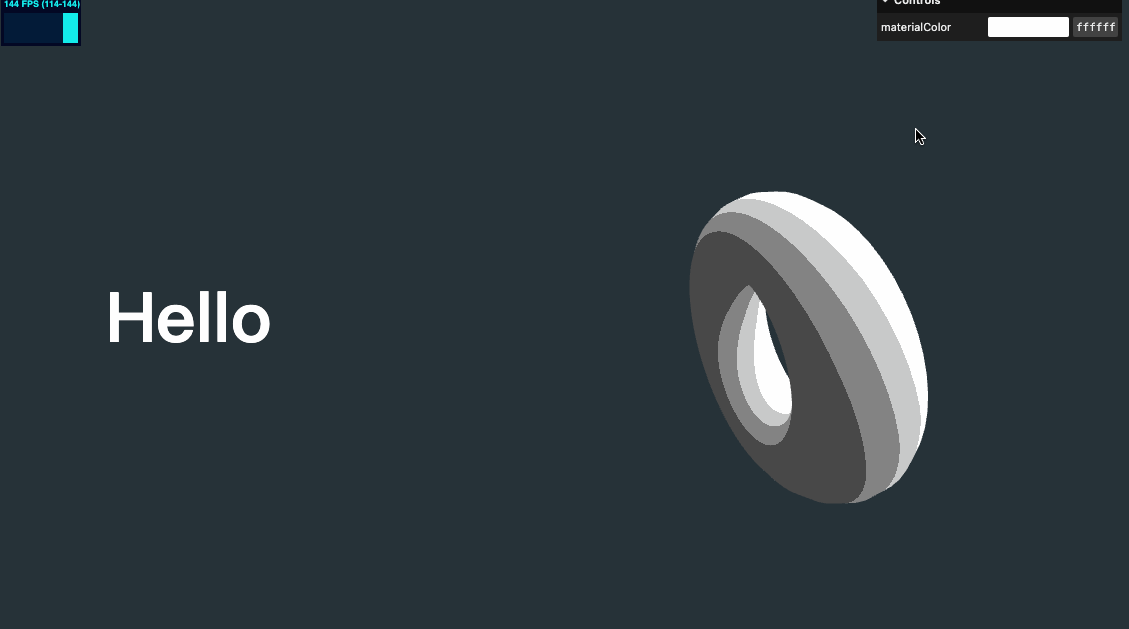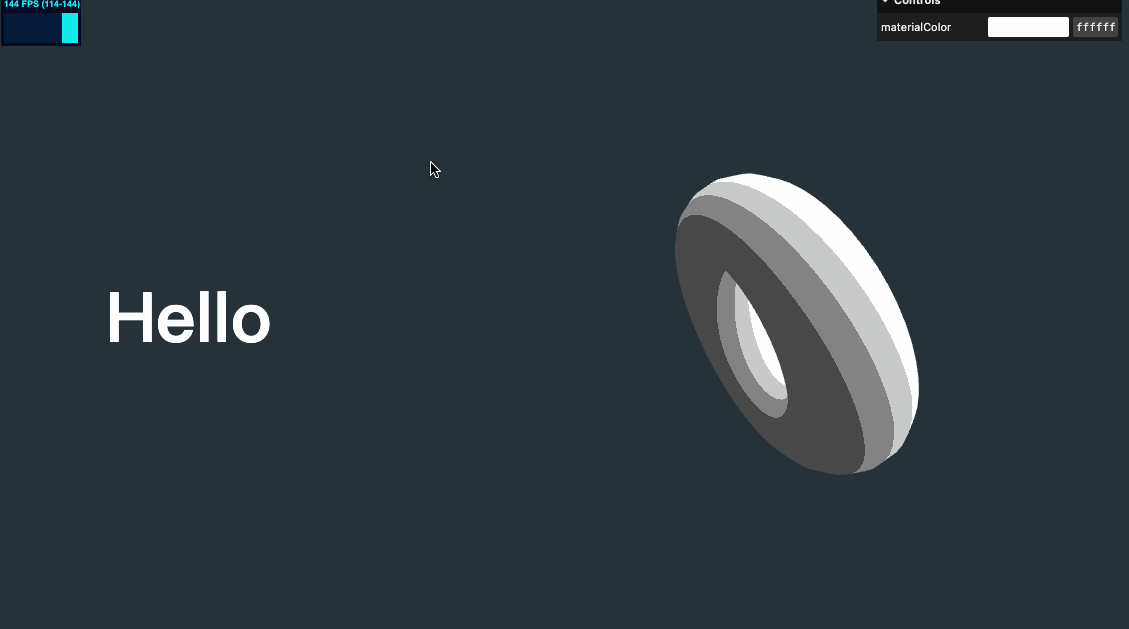
我们不能直接在 requestAnimationFrame 再修改 camera 的位置,因为之前已经设置过了滚动时相机的位移,我们不能覆盖这个位移,所以可以用一个取巧的方式,给相机增加一个 group,移动 group 达到再增加一个位移的效果
// Group
const cameraGroup = new THREE.Group()
scene.add(cameraGroup)
// Camera
const camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(75, sizes.width / sizes.height, 0.1, 100)
camera.position.set(0, 0, 4)
cameraGroup.add(camera)
// Animations
const tick = () => {
// ...
if (mouse.x && mouse.y) {
cameraGroup.position.setX(mouse.x)
cameraGroup.position.setY(mouse.y)
}
// ...
}
效果如下

缓动效果
视察效果看起来不过,但是我们想让它表现更好,可以增加一些缓动效果,更符合弹性阻尼物理效果。
这里通过 deltaTime 来进行增量位移。需要特别注意的是不能在同一个 requestAnimationFrame 里同时使用 getElapsedTime 和 getDelta。因为 getElapsedTime 里也调用了 getDelta,这是一个危险的设计。详情见 issue THREE.clock.getElapsedTime has a side effect invalidating .getDelta() #5696
所以我们要自己计算 deltaTime 代码如下
// Animations
const clock = new THREE.Clock()
let previousTime = 0
const tick = () => {
stats.begin()
const elapsedTime = clock.getElapsedTime()
const deltaTime = elapsedTime - previousTime
previousTime = elapsedTime
// const deltaTime2 = clock.getDelta()
// console.log(deltaTime);
// console.log(deltaTime2);
// console.log('----');
// Animate meshes
sectionMeshes.forEach((mesh) => {
mesh.rotation.set(elapsedTime * 0.1, elapsedTime * 0.12, 0)
})
// animate camera
camera.position.setY((-scrollY / sizes.height) * objectsDistance)
if (mouse.x && mouse.y) {
const parallaxX = mouse.x * 0.5
const parallaxY = mouse.y * 0.5
cameraGroup.position.x += (parallaxX - cameraGroup.position.x) * 5 * deltaTime
cameraGroup.position.y += (parallaxY - cameraGroup.position.y) * 5 * deltaTime
}
// Render
renderer.render(scene, camera)
stats.end()
requestAnimationFrame(tick)
}
粒子效果
粒子效果可以带来更好的沉浸体验,所以我们增加一些粒子特效,感觉到这是一个有深度的空间。
运用之前所学的知识,先将粒子效果创建出来,暂时不管位置问题
/**
* Particles
*/
// Geometry
const particlesCount = 200
const positions = new Float32Array(particlesCount * 3)
for (let i = 0; i < particlesCount; i += 1) {
positions[i * 3 + 0] = Math.random()
positions[i * 3 + 1] = Math.random()
positions[i * 3 + 2] = Math.random()
}
const particlesGeometry = new THREE.BufferGeometry()
particlesGeometry.setAttribute('position', new THREE.BufferAttribute(positions, 3))
// Material
const particlesMaterial = new THREE.PointsMaterial({
color: parameters.materialColor,
sizeAttenuation: true,
size: 0.03
})
// Points
const particles = new THREE.Points(particlesGeometry, particlesMaterial)
scene.add(particles)
效果如下

我们需要将粒子在空间内散布,所以可以将 x 和 z 轴设置的更加扩散一些。y 轴方向我们要让粒子扩散到每个 section
for (let i = 0; i < particlesCount; i += 1) {
positions[i * 3 + 0] = (Math.random() - 0.5) * 10
positions[i * 3 + 1] =
objectsDistance * 0.5 - Math.random() * objectsDistance * sectionMeshes.length
positions[i * 3 + 2] = (Math.random() - 0.5) * 10
}

滚动到区域时触发的动画
最后我们在做一些滚动到每个区域时触发的动画。我们在滚动到这个区域时,增加一些旋转动画。
/**
* Scroll
*/
let { scrollY } = window
let currentSection = 0
window.addEventListener('scroll', () => {
scrollY = window.scrollY
const newSection = Math.round(scrollY / sizes.height)
if (newSection !== currentSection) {
currentSection = newSection
console.log('changed', currentSection)
}
})
借助 gsap 创建旋转动画
/**
* Scroll
*/
let { scrollY } = window
let currentSection = 0
window.addEventListener('scroll', () => {
scrollY = window.scrollY
const newSection = Math.round(scrollY / sizes.height)
if (newSection !== currentSection) {
currentSection = newSection
// console.log('changed', currentSection)
gsap.to(sectionMeshes[currentSection].rotation, {
duration: 1.5,
ease: 'power2.inOut',
x: '+=6',
y: '+=3',
})
}
})
这里要注意,需要把原有的几何体自转从依赖 elapsedTime 改为 deltaTime
// Animate meshes
sectionMeshes.forEach((mesh) => {
mesh.rotation.set(deltaTime * 0.1 + mesh.rotation.x, deltaTime * 0.1 + mesh.rotation.y, 0)
})
效果如下

在线 demo 链接
可扫码访问

移动端适配
我们使用 CSS media query,针对纵向的手机屏幕进行适配。代码如下
/* Portrait */
@media screen and (orientation:portrait) {
section {
align-items: center;
justify-content: flex-start;
}
section:nth-child(odd) {
align-items: center;
}
h1 {
font-size: 7vmin;
color: #fff;
margin-bottom: 40vh;
}
h2{
font-size: 4vmin;
color: #fff;
margin-bottom: 6vh;
}
}
在 js 中我们也可以简单的判断宽高,来确实是手机
const isPortrait = sizes.width < sizes.height
针对手机的视角进行微调
if (isPortrait) {
camera.position.setZ(8)
objectsDistance = 11
}
// ...
sectionMeshes.forEach((item, index) => {
if (isPortrait) {
item.position.setY(-objectsDistance * index)
} else {
item.position.setX(index % 2 === 0 ? 2 : -2)
item.position.setY(-objectsDistance * index)
}
})
在手机端我们使用设备陀螺仪检测,代替 mousemove 检测
if (isPortrait) {
/**
* device orientation
*/
window.addEventListener('deviceorientation', (event) => {
const { beta, gamma } = event
if (beta !== null && gamma !== null) {
const x = (gamma || 0) / 20 // -180 :: 180
const y = (Math.min(beta || 0, 89) - 45) / 30 // -90 :: 90
console.log(x, y)
mouse.x = x
mouse.y = -y
}
})
} else {
window.addEventListener('mousemove', (event) => {
mouse.x = (event.clientX / sizes.width) * 2 - 1
mouse.y = -(event.clientY / sizes.height) * 2 + 1
})
}
iOS 监听陀螺仪无效问题
剩下的保持不变。执行上述代码后,你会发现在 iOS 设备上无效,这是因为 iOS 需要独立申请权限,需要使用 DeviceOrientationEvent.requestPermission()。我们修改代码
/**
* device orientation
*/
const listenGyro = () => {
window.addEventListener('deviceorientation', (event) => {
const { beta, gamma } = event
if (beta !== null && gamma !== null) {
const x = (gamma || 0) / 20 // -180 :: 180
const y = (Math.min(beta || 0, 89) - 45) / 30 // -90 :: 90
console.log(x, y)
mouse.x = x
mouse.y = -y
}
})
}
if (isPortrait) {
if (
typeof DeviceOrientationEvent !== 'undefined'
// @ts-ignore
&& typeof DeviceOrientationEvent.requestPermission === 'function'
) {
// @ts-ignore
DeviceOrientationEvent.requestPermission()
.then((permissionState: string) => {
if (permissionState === 'granted') {
// handle data
listenGyro()
} else {
// handle denied
}
})
.catch((err: any) => {
console.log(err)
})
} else {
listenGyro()
}
} else {
window.addEventListener('mousemove', (event) => {
mouse.x = (event.clientX / sizes.width) * 2 - 1
mouse.y = -(event.clientY / sizes.height) * 2 + 1
})
}
可以看到 iOS 依然无效,这是因为,iOS 设备必须通过用户点击的方式获取授权,不能载入页面自动申请权限。于是我们需要增加一个弹窗。代码如下
<div class="permissionDialog" id="permissionDialog" style="visibility: hidden">
<div class="title">
Request permission of motion for better animation effect
</div>
<div class="buttonArea">
<button id="cancel">Cancel</button>
<button id="allow">Allow</button>
</div>
</div>
.permissionDialog {
position: fixed;
z-index: 999;
left: 50%;
top: 50%;
margin-left: -100px;
margin-top: -75px;
width: 200px;
height: 150px;
background-color: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.7);
backdrop-filter: blur(4px);
color: #111;
border-radius: 16px;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
align-items: center;
box-shadow: 0 0 20px 2px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5);
}
.permissionDialog>.title {
width: 90%;
text-align: center;
margin-top: 20px;
}
.permissionDialog>.buttonArea {
margin-top: 16px;
width: 90%;
display: flex;
justify-content: space-around;
}
.buttonArea>button {
border: none;
outline: none;
box-shadow: 0px 0px 12px 0px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.3);
background-color: #4375cc;
border-radius: 12px;
display: inline-block;
cursor: pointer;
color: #ffffff;
font-family: Arial;
font-size: 14px;
padding: 8px 18px;
text-decoration: none;
text-shadow: 1px 0px 3px #283966;
-webkit-tap-highlight-color: transparent;
}
.buttonArea>button:active {
position: relative;
top: 1px;
}
#cancel {
background-color: #cdcdcd;
text-shadow: 1px 0px 3px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.4);
box-shadow: 0px 0px 10px -4px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5);
}
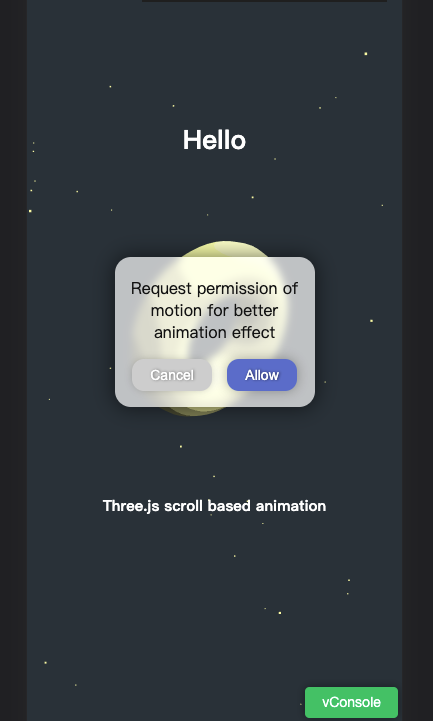
用户点击按钮时再进行申请权限
if (isPortrait) {
if (
typeof DeviceOrientationEvent !== 'undefined'
// @ts-ignore
&& typeof DeviceOrientationEvent.requestPermission === 'function'
) {
const permissionDialog = document.querySelector('#permissionDialog') as HTMLDivElement
permissionDialog.style.visibility = 'visible'
const allowBtn = document.querySelector('#allow') as HTMLButtonElement
const cancelBtn = document.querySelector('#cancel') as HTMLButtonElement
allowBtn.addEventListener('click', () => {
// @ts-ignore
DeviceOrientationEvent.requestPermission()
.then((permissionState: string) => {
console.log('permissionState', permissionState)
if (permissionState === 'granted') {
listenGyro()
} else {
// handle denied
}
permissionDialog.style.visibility = 'hidden'
})
.catch((err: any) => {
console.log('permissionState catch', err)
permissionDialog.style.visibility = 'hidden'
})
})
cancelBtn.addEventListener('click', () => {
permissionDialog.style.visibility = 'hidden'
})
} else {
listenGyro()
}
} else {
window.addEventListener('mousemove', (event) => {
mouse.x = (event.clientX / sizes.width) * 2 - 1
mouse.y = -(event.clientY / sizes.height) * 2 + 1
})
}
这样就解决了 iOS 无法调用陀螺仪的问题,只是每次需要用户手动点击授权。
增加 loading
我们需要修改 HTML 顺序,需要故意阻塞一下后续的 HTML 渲染,并增加一个占满全屏的 loading 的状态
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>scroll based animation</title>
</head>
<body style="background-color: #263238;color: #fff; font-family: sans-serif;">
<canvas id="mainCanvas" class="webgl"></canvas>
<div id="loading" style="width: 100vw;height: 100vh;display:flex;justify-content:center;align-items:center; position: fixed; top: 0;left: 0;background-color: #263238;transition: opacity 280ms ease;">loading...</div>
<script src="<%= path %>" charset="utf-8"></script>
<section class="section">
<h1>Hello</h1>
<h2>Three.js scroll based animation</h2>
</section>
<section class="section">
<h1>My projects</h2>
<h2>Sint sunt dolore architecto minima</h2>
</section>
<section class="section">
<h1>Contact me</h2>
<h2>Lorem ipsum dolor</h2>
</section>
</body>
</html>
使用 Three.js 中的 LoadingManager 处理移除 loading 的时机
const loadingManager = new THREE.LoadingManager()
loadingManager.onStart = () => {
console.log('onStart')
}
loadingManager.onProgress = () => {
console.log('onProgress')
}
loadingManager.onLoad = () => {
console.log('onLoad')
const loadingEle = document.querySelector('#loading') as HTMLDivElement
loadingEle.style.opacity = '0'
setTimeout(() => {
loadingEle.style.display = 'none'
}, 300)
}
loadingManager.onError = () => {
console.log('onError')
}
// ...
const textureLoader = new THREE.TextureLoader(loadingManager)
这样就可以得到一个很好的 loading 效果了

在线 demo 链接
可扫码访问

小结
我们学习了如何将 WebGL 的视角与 HTML 页面的滚动相结合,复习了前面所学的知识。并增加了视差效果。又增加了移动端适配,以及最后又增加了 loading 效果,整体看起来非常棒!继续加油!